FASTQ文件质控
FASTQ 文件是存储高通量测序数据的标准格式,包含了每个测序读取(read)的序列信息和对应的质量评分。原始数据会包含一些低质量reads和测序接头,因此对数据进行质控,去除低质量数据、检测测序偏差、确保数据完整性等质量控制是生信分析的关键步骤,它确保下游分析的准确性和可靠性。
常用的质控工具
| 工具名称 | 功能特点 |
|---|---|
| FastQC | 生成详细质量报告,包括碱基质量分布、GC 含量分布等 |
| fastp | 集成质量控制和过滤功能,能直接生成质量报告 |
| MultiQC | 整合多个工具的质控报告,生成一个综合性的质控报告 |
| Trimmomatic | 专注于质量剪切和接头去除,提供多种模式与灵活参数 |
| Cutadapt | 专门用于去除接头序列,支持各种复杂接头结构的处理 |
一般的质控流程
1. 初步质量评估
使用FastQC对原始fastq文件进行初步质量评估
fastqc -t 2 test_data/*.gz -o 1.fastQC/
# 结果
1.fastQC/
├── sample_1_fastqc.html
├── sample_1_fastqc.zip
├── sample_2_fastqc.html
└── sample_2_fastqc.zip
-o --outdir 指定报告输出目录,需要提前创建。
2. 查看质控报告
重点关注
-
Per base sequence quality:检查每个碱基位置的质量分布,关注是否有低质量区域(通常 Q20 或 Q30 以下)。 -
Per sequence GC content:评估 GC 含量分布是否符合预期,异常的 GC 分布可能提示样品污染或测序偏差。 -
Adapter Content:检查是否存在接头序列残留,需要在剪切时去除。
3. 质量剪切和过滤
根据 FastQC 报告,使用 fastp 或 Trimmomatic 进行质量剪切、接头去除和过滤。
fq1=sample_1.fq.gz
fq2=sample_2.fq.gz
fq1_clean=sample_1.clean.fq.gz
fq2_clean=sample_2.clean.fq.gz
fastp \
--thread 2 \
--qualified_quality_phred 15 \
--unqualified_percent_limit 50 \
--n_base_limit 10 \
--length_required 50 \
--detect_adapter_for_pe \
-i ${fq1} \
-I ${fq2} \
-o ${fq1_clean} \
-O ${fq2_clean} \
-h fastp_report.html \
-j fastp_report.json
# 结果
test/
├── fastp_report.html
├── fastp_report.json
├── sample_1.clean.fq.gz
├── sample_1.fq.gz
├── sample_2.clean.fq.gz
└── sample_2.fq.gz
trimmomatic PE \
-threads 4 \
sample_R1.fastq.gz sample_R2.fastq.gz \
cleaned_sample_R1_paired.fastq.gz cleaned_sample_R1_unpaired.fastq.gz \
cleaned_sample_R2_paired.fastq.gz cleaned_sample_R2_unpaired.fastq.gz \
ILLUMINACLIP:TruSeq3-PE.fa:2:30:10 \
LEADING:3 \
TRAILING:3 \
SLIDINGWINDOW:4:15 \
MINLEN:50
4. 整合质控报告
使用 MultiQC 整合所有样本的质控报告,便于全面评估。
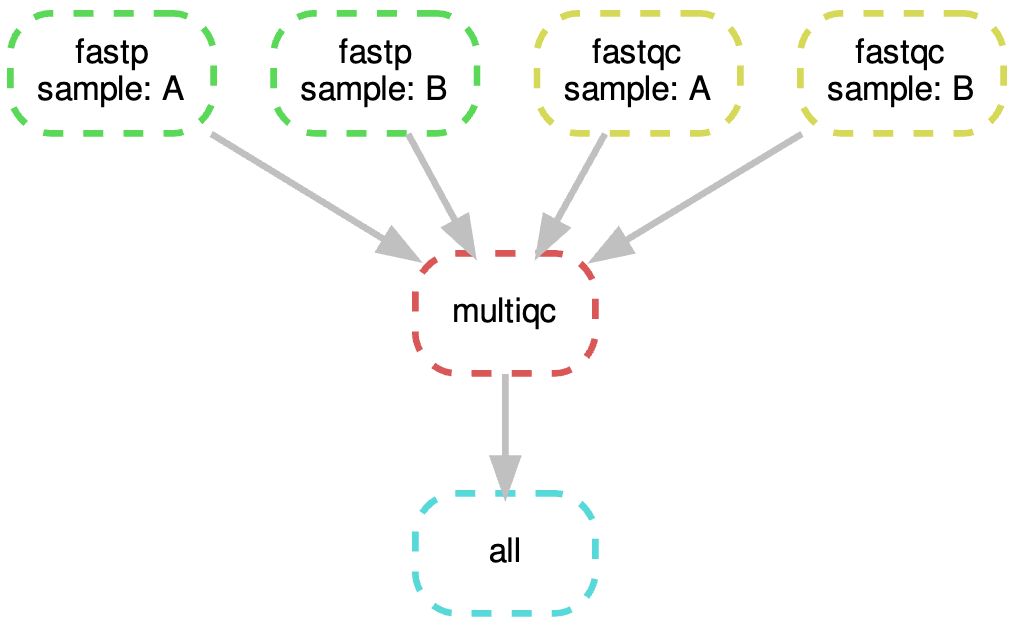
完整的snakemake流程
流程图
为了方便重复使用,传入外部文件路径,将样品信息放入 units sheet,格式如下。
# configfile
configfile: "config.yaml"
import pandas as pd
# Load units from config file. Note: the first column must be the sample name
units = pd.read_csv(config["units"], sep="\t", index_col=0).sort_index()
# get the list of samples
SAMPLES = units.index.tolist()
# define the Function to get the input files
def get_fq(wildcards, fq):
"""
wildcards: dict
The wildcards from the rule
fq: str
The file type to get. Either "fq1" or "fq2"
"""
return units.loc[wildcards.sample, fq]
# Define the rule all
rule all:
input:
"1.fastQc/multiqc_report.html"
rule fastqc:
input:
fq1= lambda wildcards: get_fq(wildcards, "fq1"),
fq2= lambda wildcards: get_fq(wildcards, "fq2")
output:
html1="1.fastQc/{sample}_1_fastqc.html",
html2="1.fastQc/{sample}_2_fastqc.html"
threads: 2
log:
"1.fastQc/logs/{sample}_fastqc.log"
shell:
"""
fastqc \
--threads {threads} \
{input.fq1} {input.fq2} \
-o 1.fastQc 2> {log}
"""
# fastp rule for paired-end reads
rule fastp:
input:
fq1= lambda wildcards: get_fq(wildcards, "fq1"),
fq2= lambda wildcards: get_fq(wildcards, "fq2")
output:
fq1="data/{sample}_1.clean.fastq.gz",
fq2="data/{sample}_2.clean.fastq.gz",
json="1.fastQc/{sample}_fastp.json",
html="1.fastQc/{sample}_fastp.html"
threads: 2
log:
"1.fastQc/logs/{sample}_fastp.log"
shell:
"""
fastp \
--thread {threads} \
--qualified_quality_phred 15 \
--unqualified_percent_limit 50 \
--n_base_limit 10 \
--length_required 50 \
--detect_adapter_for_pe \
-i {input.fq1} \
-I {input.fq2} \
-o {output.fq1} \
-O {output.fq2} \
-h {output.html} -j {output.json} 2> {log}
"""
# 规则 multiqc 使用 MultiQC 汇总 FastQC 和 Fastp质控的结果
rule multiqc:
input:
expand("1.fastQc/{sample}_fastp.html", sample=SAMPLES),
expand("1.fastQc/{sample}_1_fastqc.html", sample=SAMPLES)
output:
multiqc="1.fastQc/multiqc_report.html",
log:
"1.fastQc/logs/multiqc.log"
shell:
"multiqc 1.fastQc/ --filename multiqc_report --outdir 1.fastQc/ 2> {log}"